看大家用我的 4o-free 项目还挺开心的,想着授人以鱼不如授人以渔,出个简单的逆向教学(
# 前言
本教程需要有一定Python基础,本教程作者在Python也不算是专家,仅作为参考用
原创,首发NodeLoc,搬运通知&标出处
# 0x00 确定目标
目标最好选定那种新创公司(草台班子),这种一般都做的防护不好/没有防护,逆向轻而易举
如果遇见那种需要一堆验证的/要经常登录的/每次访问都弹CF的,建议直接放弃
(偶尔弹CF还是可以尝试)
本教程将以 https://ai-chats.org/chat/ 做示例。
# 0x01 分析请求
在网站上发起一个聊天请求,并通过Chrome(或者其他浏览器)的Devtools抓取这个请求。
(请求的Path一般都很有辨识性,如`completions`或`send`)
[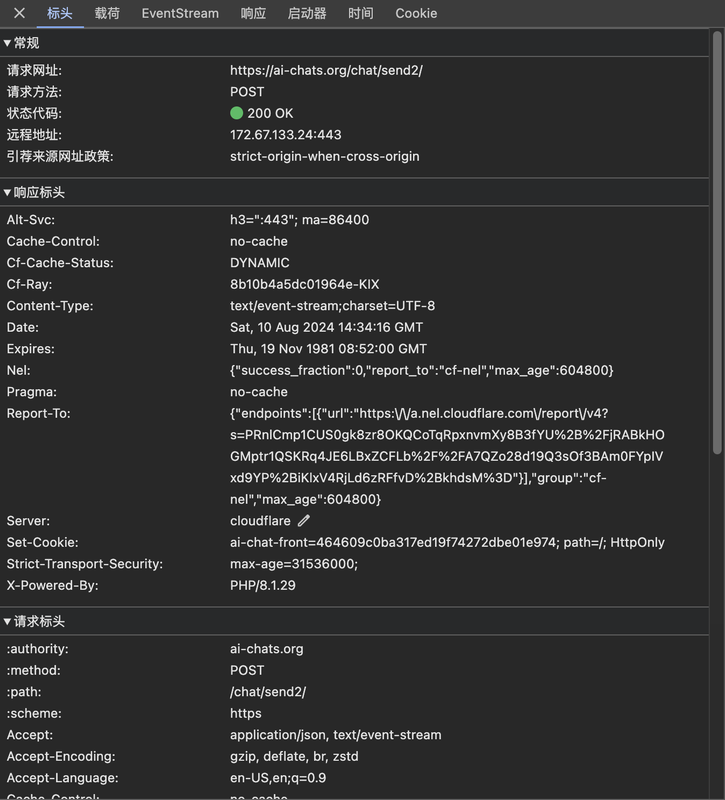
](https://postimg.cc/mhg9P31R)
接着查看“载荷”选项卡,分析请求的Payload。
```json
{
"type": "chat",
"messagesHistory": [
{
"id": "9025c8e5-15a3-4ef3-b299-5eff7e077cb9",
"from": "you",
"content": "你好啊!"
}
]
}
```很幸运,ai-chats.org的结构非常简单,我们可以看见上下文就是被包装在`messagesHistory`字段中。
接下来,我们查看多轮对话的情况。
```json
{
"type": "chat",
"messagesHistory": [
{
"id": "9025c8e5-15a3-4ef3-b299-5eff7e077cb9",
"from": "you",
"content": "你好啊!"
},
{
"id": "b0eb1255-3adc-439e-a0e7-abc1e9f5b4e7",
"from": "chatGPT",
"content": "你好!有什么我可以帮你的吗?"
},
{
"id": "23b15e51-527c-4d4d-90b3-935f9742cbfb",
"from": "you",
"content": "你是谁?"
}
]
}
```我们几乎对对话结构清楚了。对于用户发出的文本,`from`字段是`you`,模型发出的文本,`from`字段是`chatGPT`。
我们依然可以注意到:每个对话元素都有一个UUID,我们目前假设它是随机的,写出一个生成有效载荷的Python函数。
```python
import uuid
def generate_chat_payload(messages):
payload = {“type”:“chat”,“messagesHistory”:}
for message in messages:
payload[“messagesHistory”].append({
“id”: str(uuid.uuid4()),
“from”: “chatGPT” if message[“role”] == “assistant” else “you”,
“content”: message[“content”]
})
return payload
```
# 0x02 复现请求
接下来,我们要做的事情就是复现我们在浏览器中发出的请求了。
在请求这块,有一个小细节:HTTP/2请求更不容易被Cloudflare拦截。
但部分原站裸奔/小厂CDN可能不支持HTTP/2,请自行判断。
我们使用优雅的HTTP多版本请求库——`httpx`。
```sh
$ # 安装依赖
$ pip3 install httpx httpx[http2]
```接下来,我们可以使用一个很方便的工具:curlconverter.com.
我们打开Devtools,将刚刚的请求右键,点击“复制为 cURL 格式”,之后粘贴到curlconverter.com,选择Python requests。
```python
import requests
cookies = {
…
}
headers = {
…
}
json_data = {
‘type’: ‘chat’,
‘messagesHistory’: [
{
‘id’: ‘9025c8e5-15a3-4ef3-b299-5eff7e077cb9’,
‘from’: ‘you’,
‘content’: ‘你好啊!’,
},
],
}
response = requests.post(‘https://ai-chats.org/chat/send2/’, cookies=cookies, headers=headers, json=json_data)
```
这是它生成出来的代码,接下来我们对它进行一些修改,让它变为一个函数,并迁移到httpx。
```python
import httpx
def completion():
cookies = {
…
}
headers = {
...
}
json_data = {
'type': 'chat',
'messagesHistory': [
{
'id': '9025c8e5-15a3-4ef3-b299-5eff7e077cb9',
'from': 'you',
'content': '你好啊!',
},
],
}
session = httpx.Client(http2=True)
response = session.post('https://ai-chats.org/chat/send2/', cookies=cookies, headers=headers, json=json_data)
return response
print(completion().text)
```
我们运行脚本,可以看见类似如下的输出:
```
event: trylimit
data:
data:
data: 你好
data: !
data: 有什么
data: 我
data: 可以
data: 帮助
data: 你
data: 的吗
data: ?
```
这证明我们的请求成功的被服务器接受了!下一步,我们将会让它对接上我们前面写的生成上下文函数。
# 0x03 进一步适配
我们只需要把这两段代码简单的组合在一起,就能以OpenAI格式的上下文请求ai-chats.org的API了。
```python
import uuid
import httpx
def generate_chat_payload(messages):
payload = {“type”:“chat”,“messagesHistory”:}
for message in messages:
payload[“messagesHistory”].append({
“id”: str(uuid.uuid4()),
“from”: “chatGPT” if message[“role”] == “assistant” else “you”,
“content”: message[“content”]
})
return payload
def completion(messages):
cookies = {
…
}
headers = {
...
}
json_data = generate_chat_payload(messages)
session = httpx.Client(http2=True)
response = session.post('https://ai-chats.org/chat/send2/', cookies=cookies, headers=headers, json=json_data)
return response<i>
```
到这里,这个逆向出来的API基本就可以用了。但是——我们当然不希望用逆向模型的时候,弹出来一堆上下文的原始数据,不是吗?接下来,我们对completion()函数做一些修改,让其支持EventStream格式。
```python
---snip---
def completion(messages):
cookies = {
...
}
headers = {
...
}
json_data = generate_chat_payload(messages)
client = httpx.Client(http2=True)
with client.stream(
"POST", "https://ai-chats.org/chat/send2/", json=json_data
) as request:
for line in request.iter_lines():
if line.startswith("data: "):
yield {"type":"token", "data": line.split("data: ",1)[1]}
yield {"type":"end"}
for i in completion([{“role”:“user”,“content”:“你好!”}]):
print(i)
```
运行脚本,你应该能够看见类似于下面的输出:
```
{'type': 'token', 'data': ''}
{'type': 'token', 'data': ''}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '你好'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '!'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '有什么'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '我'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '可以'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '帮助'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '你'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '的吗'}
{'type': 'token', 'data': '?'}
{'type': 'end'}
```为了方便后面的Eventstream响应,我们还需要一个函数把它包装为OpenAI格式的流:
```python
---snip---
def openai_style_wrapper(messages):
created = int(time.time())
compid = "chatcmpl-AiChatsOrg-" + uuid.uuid4().hex
for message in completion(messages):
if message["type"] == "token":
yield "data: " + json.dumps(
{
"id": compid,
"object": "chat.completion.chunk",
"created": created,
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"delta": {"role": "assistant", "content": message["data"]},
"finish_reason": "",
}
],
}
) + "\n\n"
else:
yield "data: [DONE]\n\n"
---snip---
```这是我们的一大进步!我们把它包装为了一个Python装饰器,还把它的响应转化为了标准的OpenAI格式,以便我们后面把它转换为一个API。
# 0x04 2API,启动!!!
下面一步就是把你的代码适配成一个OpenAI格式的HTTP服务器了。因为这个部分有很多可能性,每个人都有每个人喜欢的框架、技术栈,我就直接贴上我的代码了。
```python
import fastapi
import fastapi.middleware.cors
import httpx
import uuid
import json
import time
AUTHOR = “0x24a”
app = fastapi.FastAPI()
app.add_middleware(
fastapi.middleware.cors.CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=[““],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=[””],
allow_headers=[“*”],
)
—snip—
@app.get(“/v1/models”)
def models():
return {
“data”: [
{“created”: 0, “id”: “gpt-4o-mini”, “object”: “model”, “owned_by”: “0x24a”}
]
}
@app.post(“/v1/chat/completions”)
async def completion(request: fastapi.Request):
data: dict = await request.json()
if data[“model”] != “gpt-4o-mini”:
return {“code”: 500, “text”: “Invaild model”} # only 4o-mini please~
messages = data[“messages”]
streaming = data.get(“stream”, False)
if len(messages) == 0:
return {“code”: 500, “text”: “Invaild message count”}
if not streaming:
content = “”
created = int(time.time())
total_tokens = 0
for i in completion(messages):
if i[“type”] == “token”:
content += i[“data”]
total_tokens += 1
return {
“choices”: [
{
“finish_reason”: “stop”,
“index”: 0,
“message”: {“content”: content, “role”: “assistant”},
“logprobs”: None,
}
],
“created”: created,
“id”: “chatcmpl-AichatsOrg2APIDemo-” + uuid.uuid4().hex,
“model”: “gpt-4o-mini”,
“object”: “chat.completion”,
“usage”: {
“completion_tokens”: total_tokens,
“prompt_tokens”: 0,
“total_tokens”: total_tokens,
},
}
else:
return fastapi.responses.StreamingResponse(
openai_style_wrapper(messages), media_type=“text/event-stream”
)
```
# 0x05 善后
后面我们还需要对模型进行IQ Test,以防模型的能力受到了削弱。
```
You: 请记住,我叫0x24a。
Bot: 好的,0x24a,你有什么需要帮助的吗?
You: 我叫什么名字?
Bot: 由于我是一个大语言模型,我无法…
```明显,我们逆向出来的没有上下文(这是因为他们官网就削掉了上下文!),我们可以用Prompt来手搓一个上下文。
```python
---snip---
def generate_chat_payload(messages):
payload = {"type":"chat","messagesHistory":[]}
generated_context = "For some reason, you've forgotten everything I've ever said to you.\nNext, I'm going to tell you about the conversation I had with you, and ask you to respond to my last sentence.\n"
for message in messages:
generated_context+=f"<|Message role=\"{message['role']}\"|>{message['content']}</|Message|>"
payload["messagesHistory"].append({
"id": str(uuid.uuid4()),
"from": "you",
"content": generated_context
})
return payload
---snip---
```我们再次测试上下文功能性:
```
You: 请记住,我叫0x24a。
Bot: 好的,0x24a,你有什么需要帮助的吗?
You: 我叫什么名字?
Bot: 你叫0x24a。有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
```# 0x06 结语
目前我们只是完成了一个“能用”的逆向API,对于代理池、多Worker防堵塞、身份验证这些就需要自己研究了。
值得一提的是,4o-free.24a.fun(https://www.nodeloc.com/d/5823)使用的就是这个逆向流程。
教程写的很急、文笔可能很烂……
如文章有错误,欢迎指出!
无论如何,希望你喜欢这篇教程!